Profile of Herod Agrippa II
Paul’s Encounter with King Agrippa
Apostle Paul On Trial by Nikolai Bodarevsky, 1875. Agrippa and Berenice are both seated on thrones.
“Agrippa said to Paul, ‘You may now speak for yourself.’ Paul lifted his hand and started to talk, ‘King Agrippa, the Jews have said many things against me. I am happy to be able to tell you my side of the story. You know all about the Jewish ways and problems. So I ask you to listen to me until I have finished. ‘All the Jews know about my life from the time I was a boy until now. I lived among my own people in Jerusalem. If they would tell what they know, they would say that I lived the life of a proud religious law-keeper. I was in the group of proud religious law-keepers who tried to obey every law (Acts 26:1-5).“
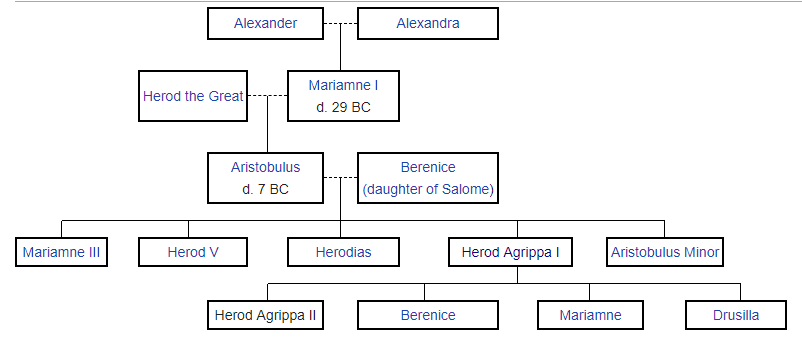
King Agrippa

Born 27/28
Died c. 92 or 100AD
Full name
Marcus Julius Agrippa
Dynasty Herodian dynasty
Father Herod Agrippa I
Mother Cyprus
Herod Agrippa II was born in the year 28, and according to a statement that is not uncontradicted (Photius, “Bibliotheca,” cod. 33), it is said that he died in the year 100. He was educated in Rome, where he saw much of the court life that had been so harmful to his father. It proved just as detrimental to him, for he reached maturity just at the time that Messalina and Agrippina dared to flaunt the most fearful depths of profligacy in public. On the sudden death of his father, the emperor Claudius desired him to enter into the full inheritance of all his rights and titles, but upon the advice of court favorites he refrained from doing so. Once again Judea was handed over to the care of procurators, and for the time being the young man was detained at court. Here he had the opportunity of being helpful to his coreligionists from time to time (Josephus, “Ant.” xv. 11, § 4; xx. 1, § 2) and of acquiring proficiency in all the arts of courtly flattery.
Succeeds Herod II. On the death of Herod II., Agrippa succeeded in having the former’s post promised him. In the year 50, without regard to the rights of the heir to the throne, he had himself appointed (“B. J.” ii. 12, § 1; “Ant.” xx. 5, § 2; 9, § 7) to the principality of Chalcis by the emperor, and also to the supervisorship of the Temple at Jerusalem, which carried with it the right of nominating the high priest. Within three years—possibly before he left Rome to assume the dignity of his office—the emperor presented him with larger territory in exchange for Chalcis, giving him the tetrarchy of his great-uncle Philip—over which Agrippa’s father had also ruled—together with that of Lysanias (Abilene), and the district of Varus (“Ant.” xx. 7, § 1; “B. J.” ii. 12, § 8). Nero, when he became emperor, added to this territory, giving him considerable tracts of Galilee and Perea.